Engine very high temperatures occur during operation. This heat must be removed from the engine. This heat is removed from the engine with air or water.
Role and Structure of Engine Cooling System
Although the engine in heat energy into mechanical energy, all the heat can be converted to power.During the time, and after each cycle consisting of a very high temperature rises. After the experiments were done, this temperature 2000 ° C – 2500 ° C ranged between. However, such high temperatures results in a very short time. Because components of the temperature of the mixture entering the thermal conductivity and the cylinder due to the low 600 ° C down to about 900 ° C.However, the engine parts can not withstand that temperature. A portion of this heat occurring in the engine, a portion of the exhaust gases are taken out from the motor by friction. On average useful heat is converted to work up to 30%. That’s the purpose of cooling the engine under all operating conditions and at all engine speeds, the engine is to keep the temperature can operate in the most efficient manner.
As we explained above, the combustion consisting end 2000 ° C – 2500 ° C as a result of excretion in different ways, the amount of residual heat on engine components should allow the engine to work regularly. The average temperature on the remaining engine components must not exceed 250 ° C. If the engine temperature rises unexpectedly tear will be more. We are as follows:
– The mechanical strength of the working engine parts is compromised.
– Piston, moving between parts such as piston rings and bearings, which necessarily leads to changes of space.
– Lubricating oil is very thin due to overheating, can not lose its viscosity and surface tension properties and functions.
– Cause more heat the cylinder head and cylinder block with the shape change causes cracking.
– Moving parts and very rapid wear of the bearings and cause them to malfunction as a result.
– Start fat burning if the temperature of the engine oil exceeds 250 ° C.
Other hand, when engine parts to run a certain temperature lower than this there are several drawbacks. So the engine will run cooler temperatures than is considered normal,
– Thermal efficiency of the engine is reduced.
– Increases in motor fuel consumption.
– Engine oil gets dirty quickly and watered. If it is
– The lack of proper lubrication,
– It leads to the formation of corrosion.
– Changes in the space of moving parts.
Accordingly, cooling system, engine operating temperature, lubrication rise as not to impair the properties of the lubricating oil and a good engine as supplied by the thermal efficiency should also be to the highest value. Cooling system with an average heat expelled from the combustion chamber is about 30%. As is apparent from this description, too much cooling of the motor is unnecessary.
A good cooling equipment;
– Should ensure that the best way to lubricate the engine.
– Must not jeopardize the mechanical strength of the engine parts.
– Needs to ensure that the highest thermal efficiency.
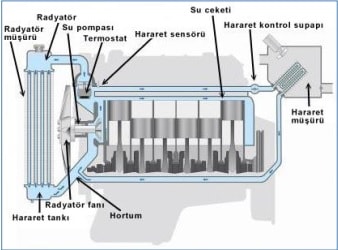
Cooling System Circuit Diagram
The first operation of the engine to reach its operating temperature quickly and with the aim of cooling equipment are additional schemes that prevent normal operation. Thus the engine to reach operating temperature as provided easily prevent inefficient operation of the engine in cold conditions and shortens time to work cold. The engine reaches normal operating temperature cooling equipment starts to normal duty.
Air Cooled Engines
Air-cooled engines, heat generated in the cylinder is transmitted directly toward the air. These engines are made separately and are grouped in a cylinder block case. cylinder and the cylinder head to increase air contact surfaces of the parts to be cooled vane is made for this purpose. If the contact surface with air replicate this surface and if the cooling airflow on how fast pass at that rate, the better. thence transmitted to the wing heat the air inside the cylinder.

Air Cooled Engines
– Cooling Benefits of Air
The cylinder block outer portions of the motor in this system, usually aluminum alloy, while the friction surface is made of steel alloy and the structure of the engine coolant does not need to be simple and light. Less space.
– Cooling the mind with Air
Course volume is not able to cool the engines with great weather. Because the amount of heat occurs in the motor, the cylinder diameter is proportional to the square of the cube and the cooling surface. cooling the engine to vary the engine speed changes in climate and cooling rate is not enough.
Steam Cooling Systems
Initially, a closed cooling system to be in the 50 to 60 ° C for jacket water outlet temperature is used is higher than 73 ° C, was considered a moderate temperature to operate an engine efficiently and well. Low result of using the coolant temperature, occurs in the cylinder jacket stone layer to prevent or mitigate possible. High temperatures up to 120 ° C utilizing the improved cooling circuit steam cooling name is given.
The cooling water is usually used with the liquid. in the cylinder block and cover are made to circulate water. This type of cooling the heat generated in the cylinder can not be given directly to the air. Block and transmits taking up heat from the water here is going through the water passage between the cover. The water passes through the heat radiator that gets around the cylinder is transmitted in the air. Thus water will be heated again and again as it returns to the bit cools the cylinder and continuous manner, it gives heat radiator, and receives heat around a roller to cool the engine is provided. Cooling water; the heat of the burned gas in the cylinder, the cylinder wall convection cooling water that passes through the liquid moving. The heat from the radiator with water, again contact with (convection) is transmitted to the radiator surface. airflow passing rapidly through the radiator, where the heat from the heated surface again take up convection. cooling system with water are in two ways. It pumps water heater is the procedure with cooling and refrigeration systems.
Water Tank Role and Structure
It called the expansion tank on the water tank. Water expansion tank, compressor compartment in the ceiling connected to each other two water tanks, with a capacity of about 650 liters. The task is to complete the diminishing water levels over time. It has a float circuit for it. Draining the water cooling system, valves and locations; locomotive chassis 4 has a drain valve on the right side. 2 is under the heating installation compartment. Engine block and drain the water in part awnings. The other two units are also under the fan compartment. They are also in the radiator ensures the drainage of water in the expansion tank in the engine block. Also during the winter months, freezing the water is drained by opening the nut of the oil cooler located under the back cover for safety, otherwise the oil cooler fires. remaining at the level of the water bottle to be emptied.

Water tank
Water Temperature Gauge Mission and Structure
The engine is running in the display showing the temperature of the liquid cooling systems.temperature of the engine by the driver is disposed in the dashboard of the vehicle it can be seen very easily. Temperature display are made in two types, steam and electric.

Temperature Gauge
Features of Coolant
Some characteristics of the water used in the system to ensure smooth operation of the cooling system with water you need to carry. If the water can cause many problems in the engine does not carry these characteristics. These problems include:
Radiators blockage, can not perform their duties due to cracking or scaling.
– The failure of cooling due to deterioration of the engine cooling surface,
– Difficulties in transporting the coolant,
– Cooling Failure to do enough,
– Many problems will emerge, especially wear on the pump with the water pressure.
The start water features to be searched for corresponds to the softness of the water. Motor 50 ppm hardness water used for cooling is considered as the upper limit. The most important factor is the minerals in the water that cause water hardness.
If in calcium, magnesium and so on. The water rate structure will increase the surplus of mineral hardness. Another feature is the cleaning of water. The engine must be extremely clean water used in the cooling system blockages are occurring in the system.
Source: MEGEP

